- Product Categories
- Industries
- About us
- Contact
Nuclear Power Plants
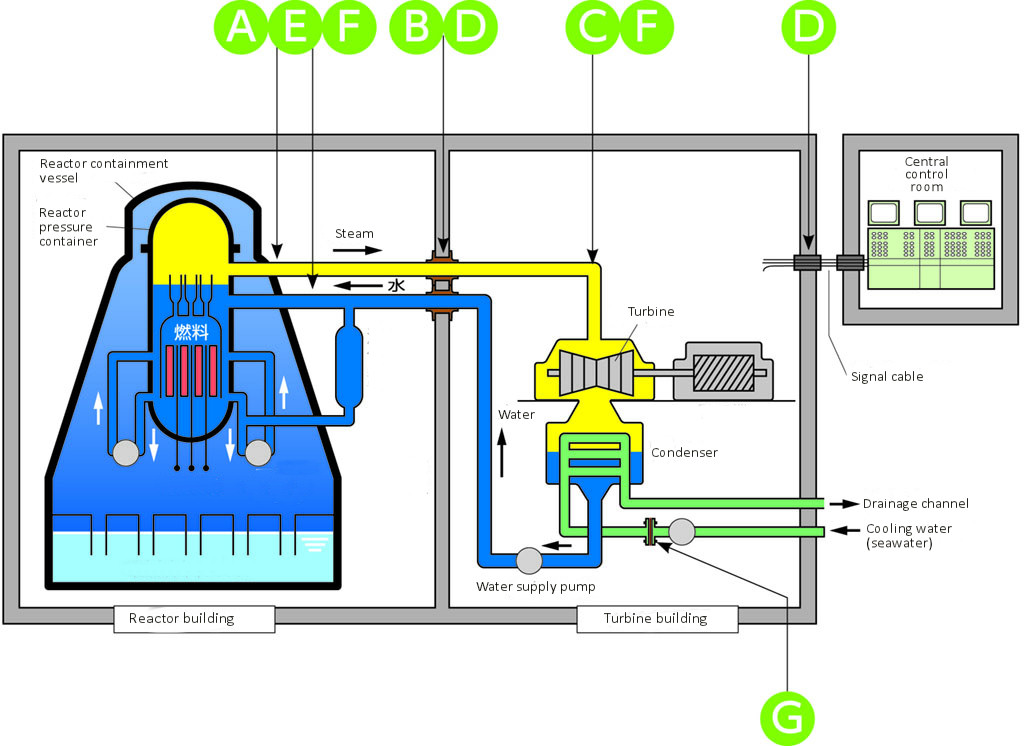
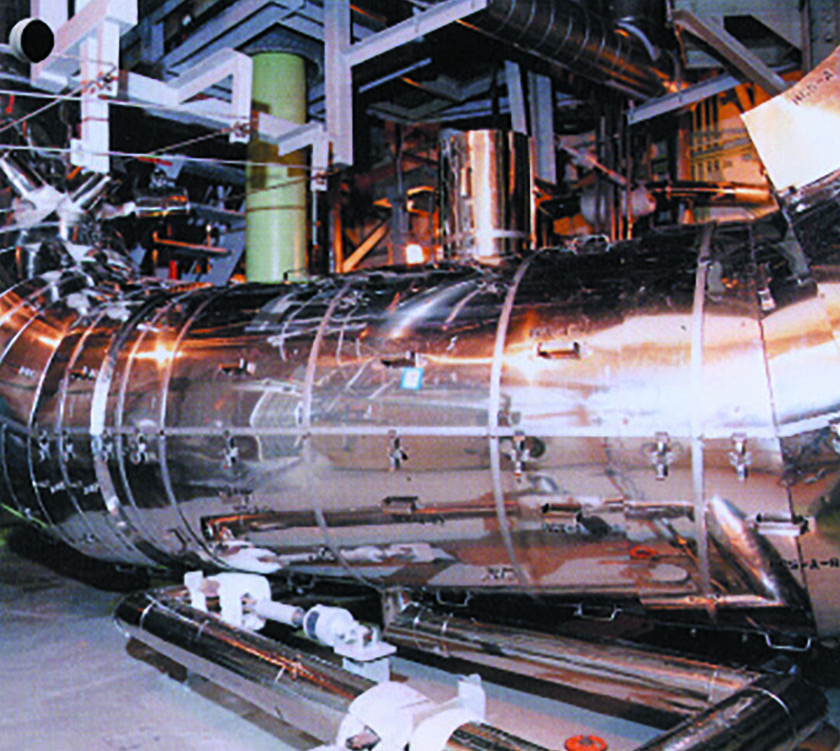
Metallic Heat Insulation
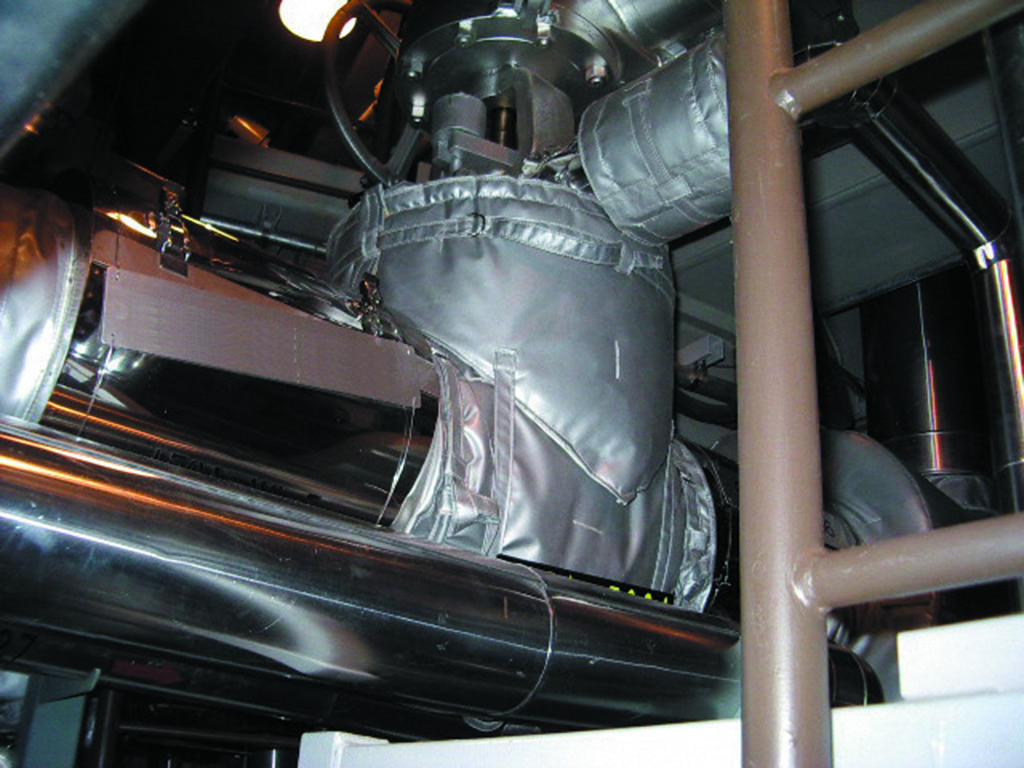
Metallic hot insulation material used for the pressure container of nuclear reactors, in recirculation equipment, and every kind of equipment and piping. There is no risk of corrosion since it is made of thin stainless steel sheet. The mechanical strength is excellent and it can be attached and detached quickly to reduce exposure when working.9999-NA NA Bellow-Q™
RNU-1015, RNU1025
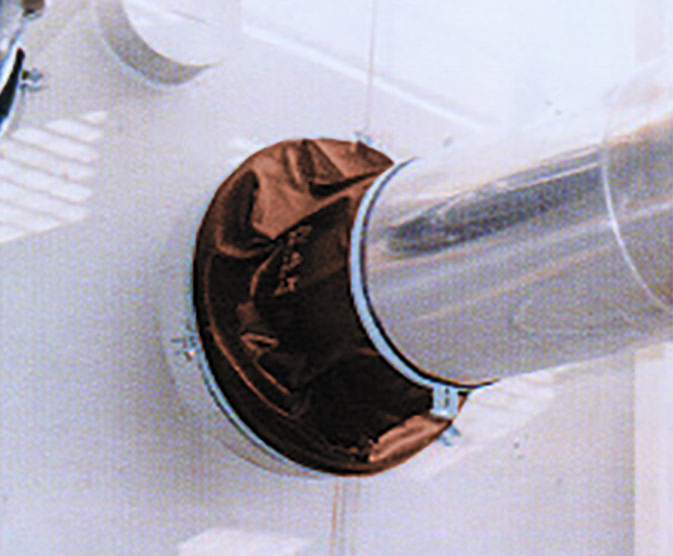
A flexible expansion joint made of special rubber material, used to seal the clearance between the pipes penetrating buildings, walls and floors and pipe holes in a nuclear power plant. this joint has excellent nuclear radiation resistance, heat resistance and flexibility, and is used as sealing material against radiation contamination air, steam generated in an accident, smoke and water generated in a fire etc.
NU MG FELT™
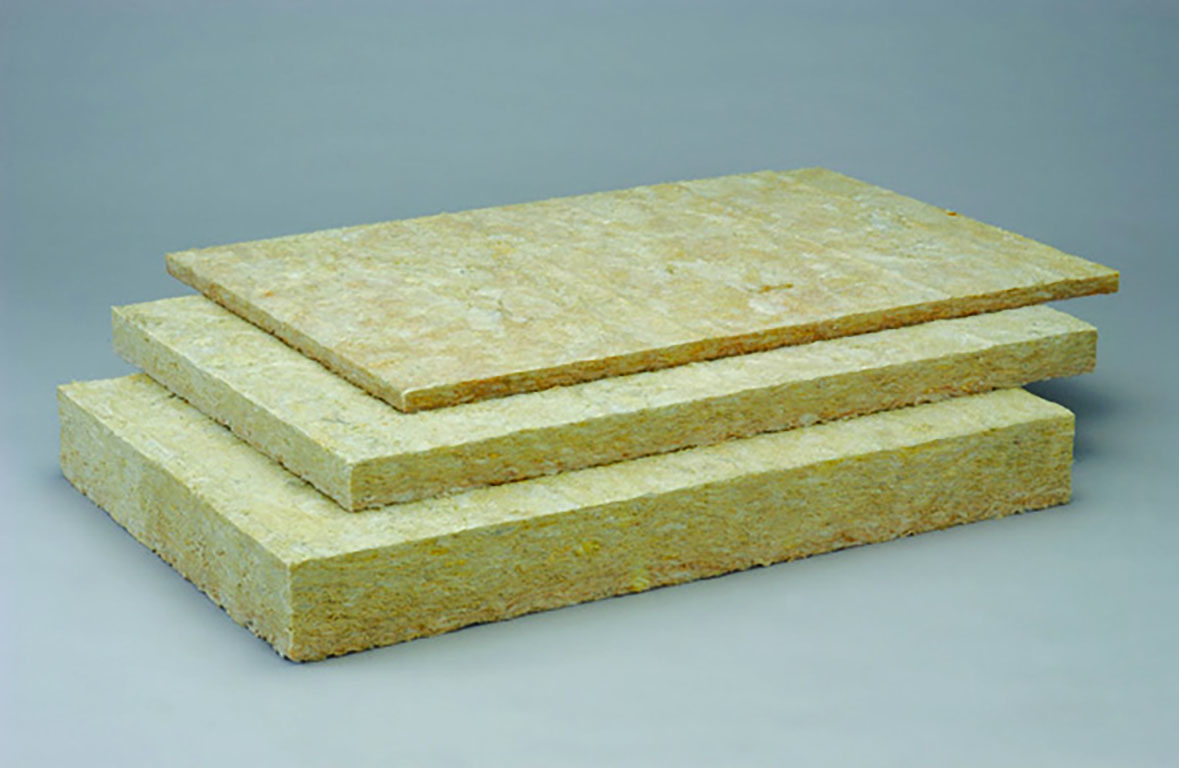
Heat insulation material made of rock wool used for piping and equipment. It is made by melting and fiberizing a mixture of slag and highly heat-resistant ore composed mostly of limestone and silicic acid. adding a binder to it, and then forming it into a board-like material.PENESEAL™ CT-18
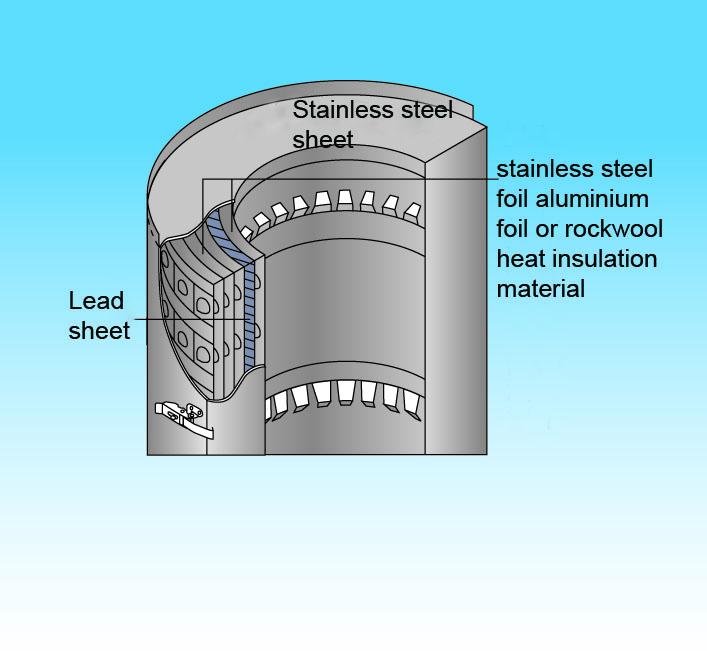
Sealing material used on walls and floors through which piping and cabling pass. It has excellent air tightness, water tightness and radiation resistance.Metallic Heat Insulation with Lead
Used as heat insulation material for applications requiring radiation shielding performance as in equipment and piping inside the reactor containment vessel. Lead sheets are combined with the metal heat insulation material.NU ENETHERMO™ K
Reusable heat insulation material for the insulation of piping, valves, flanges etc. It is suitable for areas where the insulation material must be removed during plant inspection. A waterproof type is also available for outdoor use.NU GRASEAL™ VORTEX™ Gasket
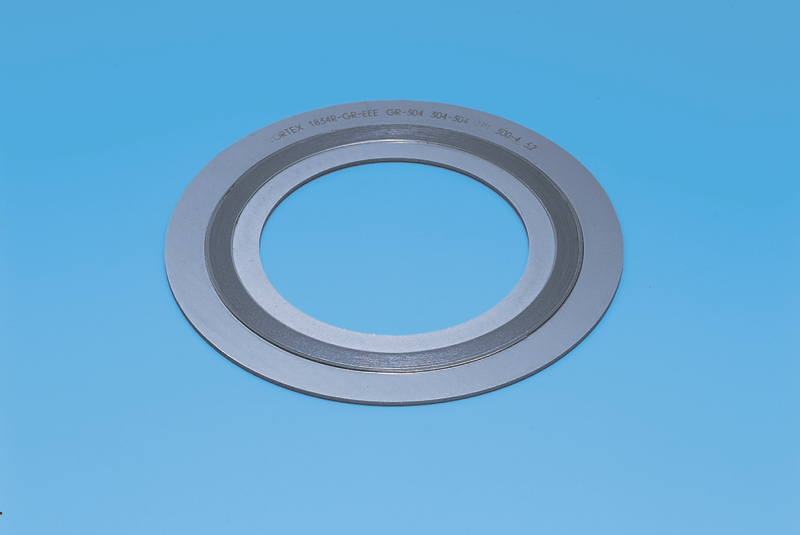
A spiral wound gasket with expanded graphite tape filter, used for pressure vessels, heat exchangers, valves and other equipment in a nuclear power plant. Suitable for the high-temperature and high-pressure conditions of the nuclear power plant; the amount of soluble chlorine, fluorine and sulfur is controlled to meet the requirements for use in nuclear power plants
* TOMBO is a registered trademark or trademark of NICHIAS Corporation.
* Name of products with "™" are trademarks of NICHIAS Corporation.
* Name of products with "™" are trademarks of NICHIAS Corporation.

 Enlarge image
Enlarge image
 Enlarge image
Enlarge image
 Enlarge image
Enlarge image
 Enlarge image
Enlarge image
 Enlarge image
Enlarge image
 Enlarge image
Enlarge image
 Enlarge image
Enlarge image